Experimental study of moisture uptake of polyurethane foam subjected to a heat sink below 30 K
Abstract
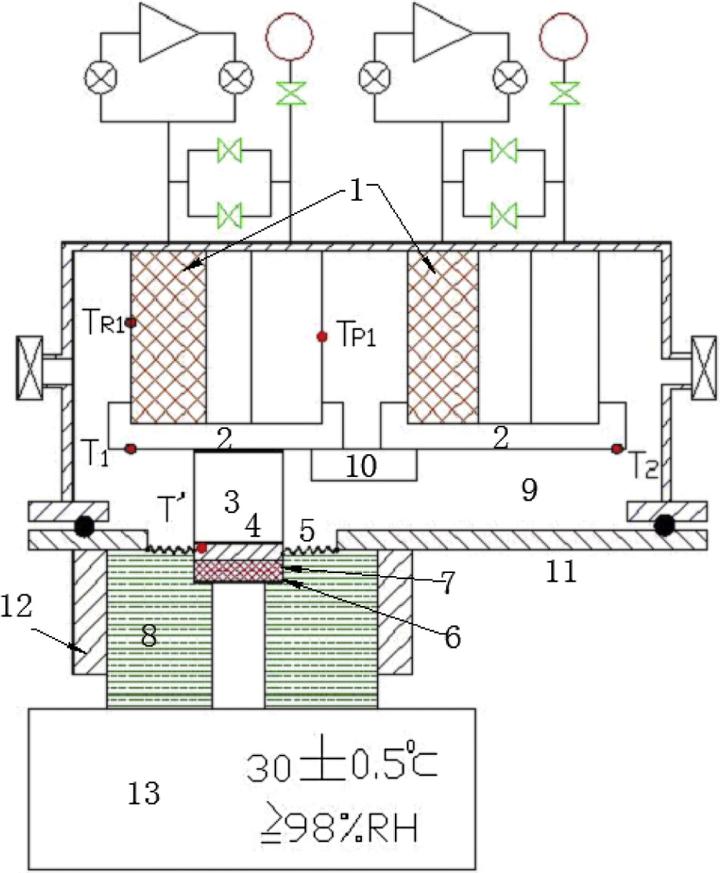
Rigid closed-cell foam is widely used to thermally insulate liquid hydrogen and oxygen tanks of space launch vehicles due to its lightweight, mechanical strength and thermal-insulating performance. Up to now, little information is available on the intrusion of moisture into the foam that subjects one side to liquid hydrogen temperatures and the other side to room temperatures and high relative humidity. A novel cryogenic moisture uptake apparatus has been designed and fabricated to measure the moisture uptake into the polyurethane foam. For safety and convenience, two identical single-stage pulse tube cryocoolers instead of liquid hydrogen are used to cool one side of the foam specimen to the lowest temperature of 26 K. Total of eight specimens in three groups, according to whether there is a butt-joint or weathering period, are tested respectively for both 5 h and 9 h. The additional weight due to moisture uptake of the foam for the 26 K cases is compared to previous measurements at 79 K. The results are instructive for the applications of foam to the insulation of liquid hydrogen tanks in space launch vehicles.